Area of Origin: Calculation and Interpretation
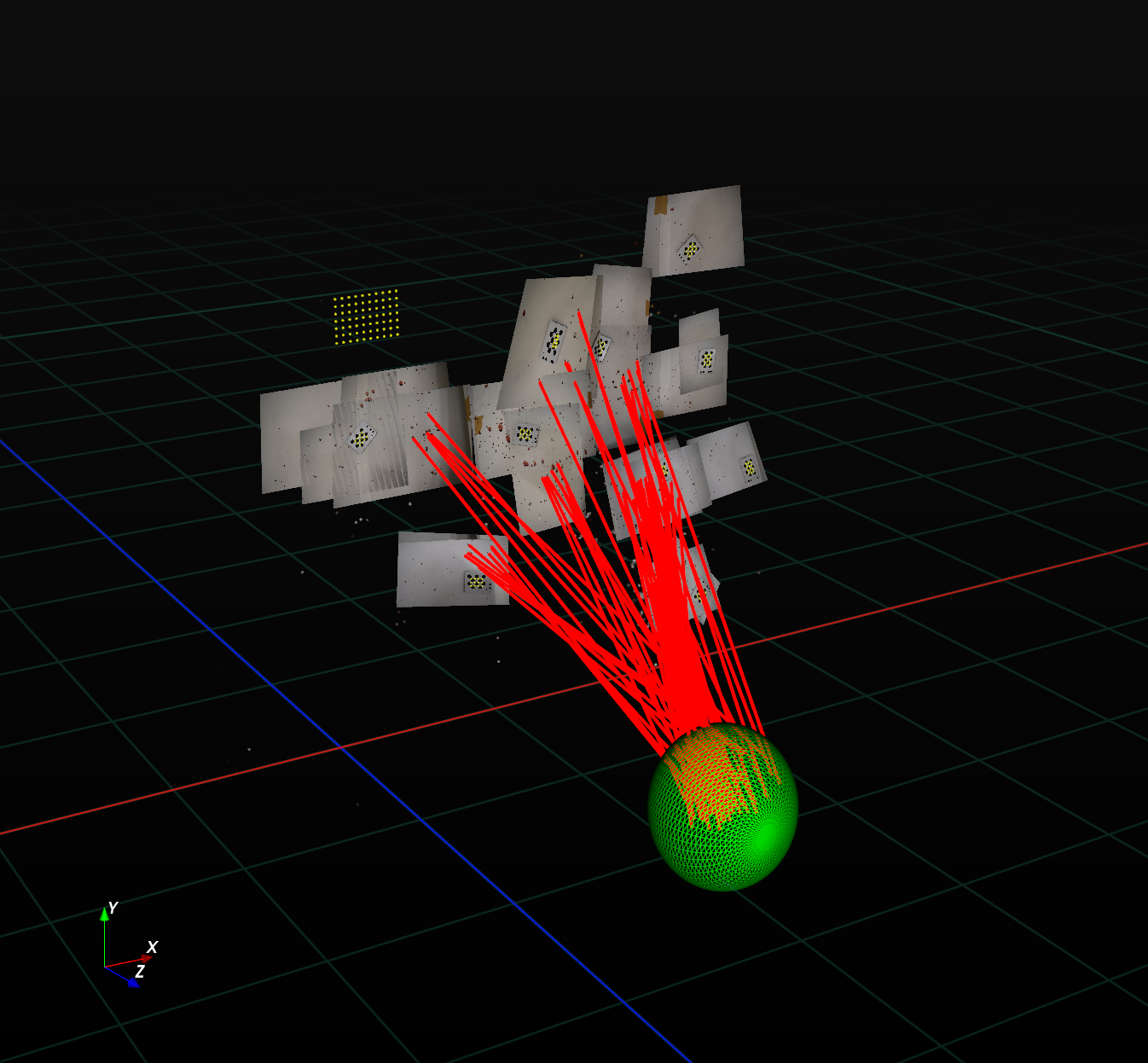
Given a set of trajectories from an impact pattern, we can examine them to determine the Area of Origin (AOO) — the point where the trajectories converge. This area helps in understanding the dynamics of the impact, and is represented as a 3D ellipsoid.
Calculation of the Area of Origin
The calculation of the AOO involves a mathematical function that is minimized. At its core, the method optimizes the placement of the ellipsoid by minimizing the sum of the squares of all angles between the stain trajectories and the lines connecting the center of the ellipsoid with each stain's coordinates.
Here’s how the process works in more detail:
Ellipsoid Center Calculation:
- The ellipsoid's center is determined by finding the point that minimizes the angular deviation between the trajectories of the stains and the lines drawn from each stain to the ellipsoid center.
Ellipsoid Size Determination:
- To define the size and shape of the ellipsoid, the closest point along each trajectory to the ellipsoid center is calculated.
- The horizontal spread of the ellipsoid is determined by calculating the standard deviation of these closest points in the horizontal plane (xz-plane).
- The vertical spread is obtained by calculating the standard deviation in the vertical direction (y-axis).
Both spreads are then used to draw the ellipsoid (of course, the spread for the x- and z-dimensions will always be the same). For a more detailed explanation of the underlying mathematical principles and the full methodology, please refer to the full publication here: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0379073824002214
Interpretation of the Area of Origin
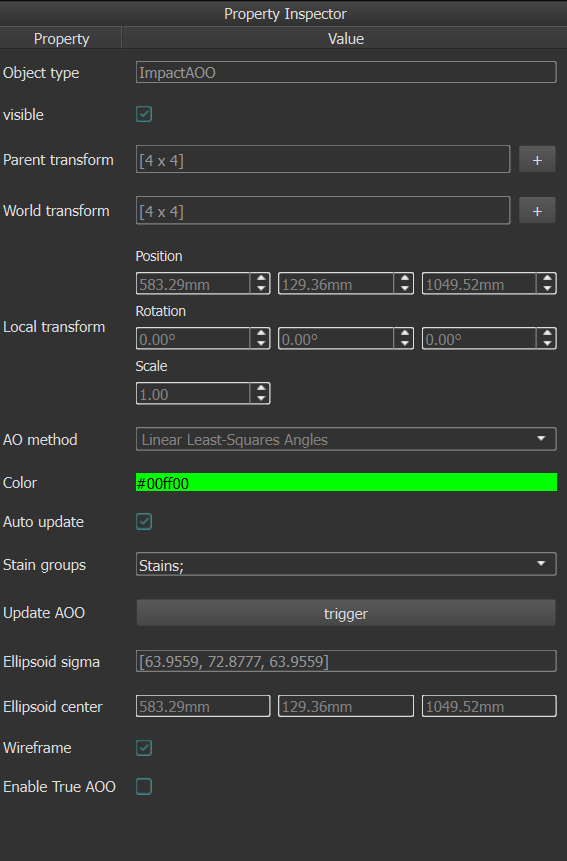
The 3D ellipsoid representing the AOO has two key properties: the center and the spread, both of which are defined in three dimensions.
Center:
- The center of the ellipsoid indicates the exact center of the Area of Origin. This is expressed in world coordinates, as per the units specified in the project settings.
Spread: * The spread represents the uncertainty of the AOO. It is derived from the standard deviation of the closest points along each stain trajectory to the ellipsoid center. * The uncertainty is quantified separately for horizontal (xz-plane) and vertical (y-axis) directions, providing insight into the variation of the calculated Area of Origin. * Note that the ellipsoid in the 3D view is drawn using 3 times the standard deviation. For example, an ellipsoid with a horizontal sigma of 2cm will have a total width of 12cm (3 times the sigma in both positive and negative direction).